Looking for a treatment ?
Find a practice for a treatment near you.
You are here
00 - Overview
SEE ALL
CHAPTERS
Overview
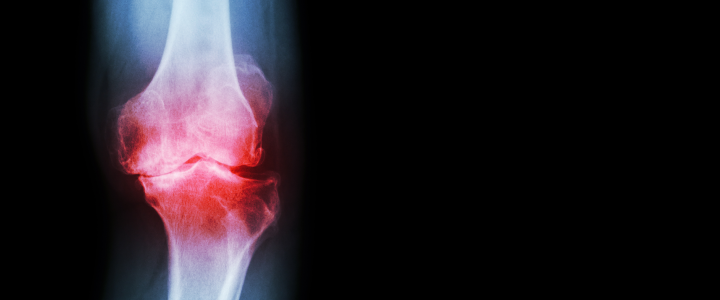
What is knee osteoarthritis?
Knee osteoarthritis, most often referred to as knee pain, is the most common joint disease and a significant cause of knee pain. This limiting condition describes the progressive degeneration of the joint cartilage, which acts as a natural cushioning absorbing the shocks and providing a smooth, gliding surface. Once the cartilage wears out, the bones rub together closely, causing pain, swelling, and stiffness. Considering that knee osteoarthritis is a degenerative pathology, it is impossible to return to a pre-injury state. However, radial shock wave therapy and other methods allow you to reduce pain and improve function effectively, and in turn, substantially improve your quality of life.
Knee osteoarthritis can be congenital (existing at birth but not inherited) or mechanical origins (comes with knee usage and time).
The most common manifestations include joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and muscle weakness. Knee osteoarthritis is associated with a considerable physical disability as simple activities such as walking, climbing stairs, and sitting or rising from a chair become too painful to perform.

Are you at risk of developing knee osteoarthritis?
Contrary to the commonly held notion, knee pain is not limited only to the elderly population.
It is estimated that knee osteoarthritis is ranked among the top 20 diseases in the 40–45 years age group [1].
Regarding gender, women are not only more likely to develop knee pain, but they also experience a more severe form of this debilitating joint disease.
Numerous factors contribute to the development of osteoarthritis:
- Older age: The median age at knee OA diagnosis is 55 years. Age-induced changes, such as cartilage thinning, weak muscle strength, and poor proprioception, increase the risk of knee osteoarthritis
- Menopause: Hormonal changes due to menopause increase the risk of knee
- Excess weight: each pound of weight added results in a 4-fold increase in the load exerted on the knee per step during daily activities.
- The lack of physical activity weakens knee muscles, which are known for their supportive and shock-absorbing role. Physical activity (at least 45 total minutes/week of moderate intensity) with low impact on the lower extremities can prevent the development of knee osteoarthritis.
- Traumatic knee injuries are one of the strongest risk factors for knee osteoarthritis.
- Genetics: almost 100 different DNA variants have been associated with knee osteoarthritis
- Specific sports involving heavy lifting or excessive load exerted on the knees (soccer players, runners, competitive weightlifters, wrestlers),
- Occupations requiring frequent knee movements and handling heavy weights.
What are the symptoms of knee osteoarthritis?
If you have been suffering from knee osteoarthritis, there are multiple symptoms that you can easily recognize and which may lead you to consult a healthcare provider for professional treatment:
- Restricted knee function
- Pain increases with activity
- Stiffness (especially morning stiffness),
- Decreased range of movement
- Knee swelling
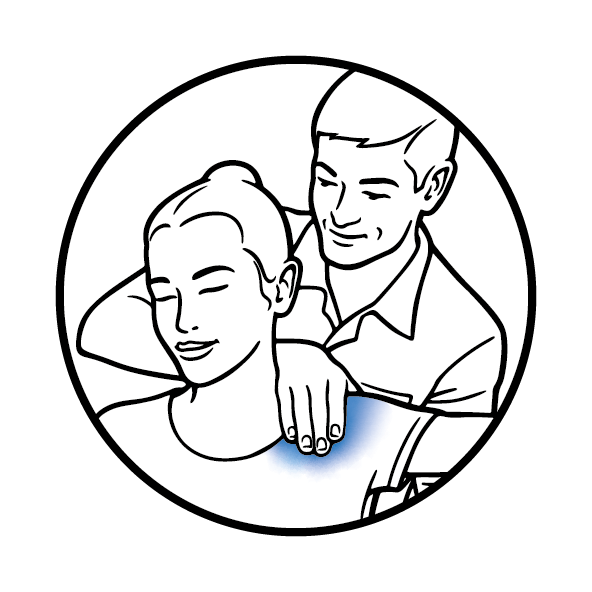
Relieve Knee Osteoarthritis Pain with Guided DolorClast® Therapy - A Non-Invasive Solution
Knee osteoarthritis can be a painful and disruptive condition. But don't lose hope! Guided DolorClast® Therapy is a treatment concept that gives practitioners the tools to deliver effective and optimized results using radial and focused shock wave therapy and laser therapy. This non-invasive and safe approach to managing knee osteoarthritis symptoms can provide relief. To find a certified practitioner near you, you can check out the Guided DolorClast® Therapy practitioner map. Don't let knee pain hold you back any longer.